✅알고리즘 2주차✅
📌 Array vs LinkedList 📌 : 중요한 개념이니 잘 숙지!

- Python 의 list 는 array 로 구현되어 있다. -> 내부적으로 동적 배열이라는 걸 사용해서, 배열의 길이가 늘어나도 O(1) 의 시간 복잡도가 걸리도록 설계되어 있음.
📍Linked List 📍
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self, value):
self.head = Node(value) # head 에 시작하는 Node 를 저장.
def append(self, value): # LinkedList 가장 끝에 있는 노드에 새로운 노드를 연결.
cur = self.head
while cur.next is not None: # cur의 다음이 노드의 끝에 갈 때까지 이동.
cur = cur.next
cur.next = Node(value)
def print_all(self): # LinkedList의 모든 원소를 출력하는 메소드.
cur = self.head
while cur is not None:
print(cur.data)
cur = cur.next
def get_node(self, index): # LinkedList의 원소를 찾는 메소드.
node = self.head
count = 0
while count < index:
node = node.next
count += 1
return node
def add_node(self, index, value): #LinkedList에 원소를 추가하는 메소드.
new_node = Node(value)
if index == 0:
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
return
node = self.get_node(index - 1)
next_node = node.next
node.next = new_node
new_node.next = next_node
def delete_node(self, index): #LinkedList의 원소를 삭제하는 메소드.
if index == 0:
self.head = self.head.next
return
node = self.get_node(index - 1)
node.next = node.next.next
linked_list = LinkedList(5)
linked_list.append(12)
linked_list.print_all()
linked_list.get_node(0)
linked_list.add_node(0, 3)❗️맨 뒤에 노드까지 가려면? : head를 따라서 이동해야하는데 head를 변경시킬 수는 없으니 cur이라는 새로운 변수 선언.
-> 맨 뒤의 노드까지(맨 마지막 노드는 다음 노드가 없으니까 아무것도 가리키지 않음 ==> cur.next == None.
📍이진탐색📍
이진탐색이란 ? : 앞에서부터 순차적으로 탐색하는 순차탐색 대신 숫자 범위의 절반을 나누어 확인하고 또 남은 범위의 절반을 확인해서 결과를 찾아가는 방식이다.
예제 코드
finding_target = 14
finding_numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16]
def is_existing_target_number_binary(target, array):
current_min = 0
current_max = len(array) - 1
current_guess = (current_min + current_max) // 2
find_count = 0
while current_min <= current_max:
find_count += 1
if array[current_guess] == target:
print(find_count) # 3!
return True
elif array[current_guess] < target:
current_min = current_guess + 1
else:
current_max = current_guess - 1
current_guess = (current_min + current_max) // 2
return False
result = is_existing_target_number_binary(finding_target, finding_numbers)
print(result)- 시간복잡도 (이진탐색 vs 순차탐색)
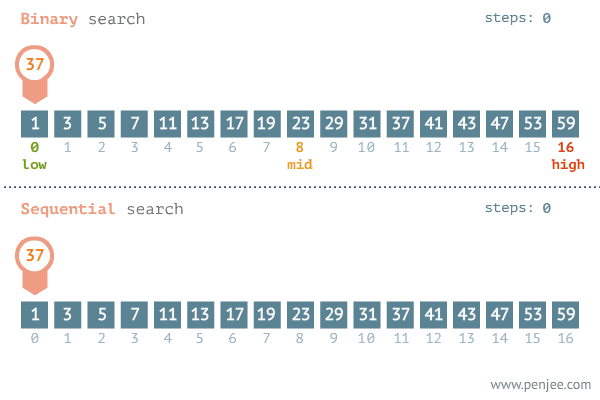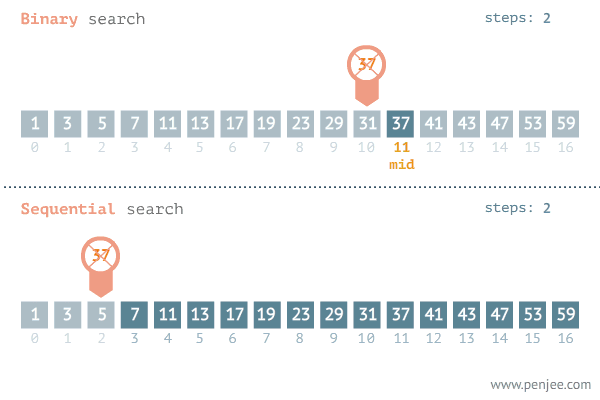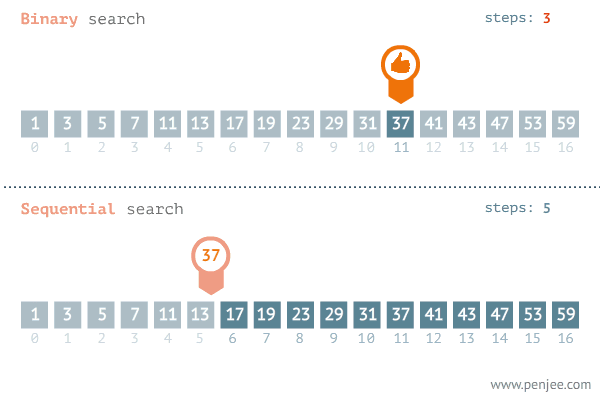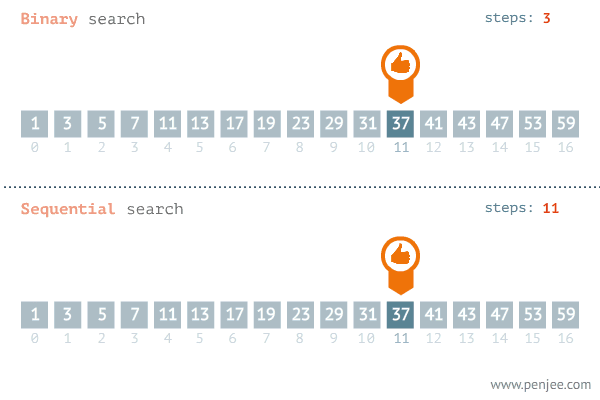
📍재귀함수📍
재귀함수란? : 자기 자신을 호출하는 함수
❗️탈출조건을 만들어줘야 재귀함수의 반복을 멈출수 있다❗️
- 팩토리얼(Factorial)
def factorial(n):
if n == 1:
return 1
return n * factorial(n - 1)
print(factorial(4)) # 24- 회문검사 (회문 : 똑바로 읽으나 거꾸로 읽으나 똑같은 단어나 문장)
input = "abcba"
def is_palindrome(string):
if len(string) <= 1:
return True
if string[0] != string[-1]:
return False
return is_palindrome(string[1:-1])
print(is_palindrome(input))
'Other > 알고리즘&자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 알고리즘 | 알고리즘 개념_3 (0) | 2022.09.21 |
|---|---|
| 알고리즘 | 알고리즘 개념_1 (0) | 2022.09.20 |